Andalusite Gemstones
Black Star Sapphire Gemstones
Cobalt Spinel Gemstones
Diopside Gemstones
he Blue Sapphire is king of Sri Lankan gems. The 400 carat Blue Sapphire called “Blue Belle”

Fred Mayer/Getty Images
This uncut diamond, embedded in river gravel, went on display at the Kimberley Diamond Museum in South Africa.
Let's say you want to find some malachite specimens to add to your gem collection. This mineral is often found near limestone and copper deposits and, within the United States, is most often found in Arizona[source: Cook and Kirk). Or maybe you're looking for the big score and want to find a diamond. Because diamonds are created under extreme pressure, they form deep within the Earth. They're most common in areas where deep mantle rocks have been pushed to the surface by geological processes. They can also be found in the alluvial deposits (rocks and soil deposited by water) along rivers that flow from these areas.
Minerals formed in Earth's mantle can find their way to the surface over the span of millions of years due to huge geologic effects such as tectonic plate upheaval. Earthquakes and volcanoes can bring deep rocks to the surface, while wind or water erosion gradually wears down surface soils to reveal buried bedrock. Humans can reveal bedrock as well, which is why it can be very rewarding to hunt for gems neartunnels, railroads or construction sites (if you're allowed).
There are numerous gem and mineral guidebooks available, many of them designed to fit in a pocket or backpack. These guidebooks can help you distinguish and identify specimens, especially because the rough forms of gems look very different from the gleaming jewels we typically imagine. In rough form, gems are partly or wholly encased in other material, usually rock. They may resemble translucent lumps or have a more defined shape, depending on the crystalline structure of the mineral. If possible, bring experienced gem hunters along on your first trip. They'll know how to spot certain minerals, and their knowledge will go beyond what you can learn from a book. You could also learn more by visiting a local museum that features samples common to the region.
For every gem in the world, there's a different way to find it. Australian sapphires are found in a certain region covered with alluvial deposits. They're strewn throughout a gravel layer beneath the topsoil. Gem hunters dig through the gravel layer and filter the rocks by putting them in a pan and shaking them in water. Because sapphires are heavier than most rocks, they tend to settle to the bottom of the pan. When the pan is flipped over and emptied, any sapphires will be sitting on top.
Panning for gold also relies on the weight of the mineral. Flakes and pellets of gold can be found mixed with gravel and sediments. Gold is heavier than water, so shaking a pan full of dirt, rock and water settles any gold to the bottom. The other material can be washed over the side, leaving the gold behind. Sluices are long channels (like miniature waterslides) with ridges on the bottom. Large volumes of dirt, rock and water course down the sluice, leaving heavy gold caught in the ridges.
There are tens of thousands of types of minerals in existence. And even though the varieties we would call gems are fewer, they're created under combinations of conditions so vast as to be nearly infinite. Pressure, heat, location, the presence of other minerals and impurities, water, and geologic forces exerted later all contribute to the hardness, clarity, crystalline structure and color of gems and minerals. That's what makes them so rare.
You'll need a lot more than a guidebook to discover hidden treasures and buried jewels. Find out what gear you should bring in the next section.
They are hoping for more foreign participation at the 'Facets' exhibition to be held in Colombo this September by gem exporters and the Gem and Jewellery Association (SLGJA).
Russia would be a key market the industry is targeting this year.
"This year for the first time we have looked at the Russian market and we are expecting a substantial delegation," Chanaka Ellawala, who chairs the 'Facets exhibition committee said.
"I would say the main focus this year is to bring dealers from the Russian market."
The annual exhibition is being held for the 19th time this year with around 150 dealers taking part in the event.
Hasitha Thilakaratne, the chairman of the National Gem & Jewelry Authority (NGJA) said authorities are trying to attract alternative markets like China, India, Russia and Brazil.
"So we are looking at markets out side USA."
Ellawala said the industry aims to go beyond cutting and polishing gems to even the extent of setting up a lab which will increase the value of the island's gems in international markets.
This year American Indian motifs seems quite attractive and since jewelry in 2009 is BIG, let’s say they fit perfectly in the picture. The typical American Indian jewelry is characterized by several iconic features like: feathers, vultures, it is usually silver with turquoise and red beads. For the more knowledgeable public the American Indian jewelry is divided in various types like Navajo or Zuni.
Here are some examples of Navajo turquoise bracelets by Andy Cadman:





Navajo rings are just as beautiful and you can find them on Chacodog:



Santo Domingo Pueblo and Zuni earrings:




The key of knowing “how to choose earrings” is to find the ones that complement your face. Because earrings are a fantastic way to enhance your appearance or to complete an outfit you must remember that they must always add balance and shape to your face. Here are some tips that will have you quickly on your way of finding the right earrings.
Round faces need earrings to provide length, such as long, dangling or rectangular-shaped earrings. Since the vertical lines emphasizes more on length, the face begins to look slimmer and longer.

People with oval-shaped faces are the most lucky ones. Their faces are very proportionate and they can wear almost any style of earrings to enhance their appearance.
Rectangular-shaped faces have more length than width and need earrings that do not emphasise length. Small studs work well and long dangling earrings should be avoided.
As long as you avoid harsh angles and square shapes, you can wear just about anything in the earring category. Hoops and curved edges will add the necessary roundness, and drop earrings, long tear drops, or multi-tiered dangling earrings will give a square shape some length.
Sharp features: Wear round earrings or earrings with curves in order to sweeten up your face shape (hoops or round beaded earrings). The curves soften the features over all to enhance and create a very flattering look for women with such sharp features.
Flat Features: The best way to sharpen face shapes with flat features is to wear angular earrings. Earrings with points like stars, triangles, and diamonds work well with women with flat features. You can have some extra fun with geometric shaped earrings.
Petite women need earrings that bring the viewer’s eye up. They have to choose earrings that compliment their size. It’s important paying attention to dangling earrings (and the space between the ears and shoulder). Longer earrings will block that space and give the appearance of a shorter neck line.
Ladies of average height are not restricted by height. They can wear any style of earrings that also flatters their face shape.
Tall women need to pay attention to the space between their ears and shoulder also. They need earrings that don’t get lost in that space such as long, dangling styles.
Here’s a small guide on How to Choose your Necklace according with the dress neckline. It is important to know the basics on choosing the pendant or necklace. Your look must have equilibrium and a bit of harmony in order to appear stylish and graceful. Good luck!

Remember that while a sparkling triple-tier necklace might look dazzling on its own, it might totally clash with your overall look. So whether you choose to drape yourself in diamonds or wrap your neckline in pearls, take the time to consider the design of your dress and your hairstyle before making any decisions.
If you had one thousand piles of diamonds and one thousand diamonds in each pile, only one of those diamonds would be a 1-carat diamond. It would take 5 times that quantity to find a 2 carat stone. DeBeers, the world’s diamond supplier, has no answer to the question how many stones have to be mined to get a 3 carat stone. 80% of all diamonds mined are industrial quality; only 20% are gem-quality. Gem quality diamonds are found in only four places world-wide: Africa, Russia, Australia and Canada

Mining Cost: 250 tons of earth must be removed to find one 1-carat stone. (a one carat diamond is the size of a pea and weighs only one-fifth of a gram). Diamonds are the most sought after substance on earth. Diamond miners have invested into state-of-the-art technology to search for diamonds where only explorers have gone before. They have developed equipment to dive to the darkest depths of the ocean and sweep the ocean floor.
What is an organic gem stone:
Some stones that are commonly used in jewelry are not onsidered gems.
Organic compounds are among the most complex in nature. Many students in the sciences consider organic chemistry a bigger stumbling block than physics or calculus.
The organic gem stone can be classified in two distinct groups; fossilized and contemporary.
Fossilized organic gem stones:
These are stones made of once living tissue that has been changed over time by natural forces into its current gem quality form.
Amber is a stone formed from a tree sap fossilized over thousands or millions of years.
Amber is usually clear with a yellowish color.
This stone resembles and is named after ambergris, a sweet smelling secretion of the sperm whale once used in perfume making.
Examples of amber containing perfectly preserved insects have been found and are considered very collectible.
Jet is also called lignite, it is a type of coal. Like coal, it is formed from ancient deposits of decaying wood under extreme pressure.
Jet formed in fresh water is called soft jet, while jet formed in salt water is called hard jet.
Like its cousin coal, jet is a shiny black stone. The English phrase 'jet black' comes from this organic gem stone.
Ammolite is the fossilized remains of ancient sea anemones. Ammolite is similar to the opal in appearance and often has a cracked or mottled surface. This cracking can give the stone the look of 'dragon scales' or a stained glass window.

These are gems made from once living tissue taken from or left behind by creatures living in our time.
Since they do not show the effect of eons of natural forces, some collectors do not consider these true gem stones. This, however, has a little effect on their popularity in jewelry.
Pearl, resembling a small marble, is usually associated with the oyster, although it is found in other mollusks as well.
At the center of each pearl is a small piece of sand or rock, which had found its way into the oyster's shell. The oyster attempts to soften the irritant by coating it in with calcium compound.
Over time, layer by layer, the pearl is formed. While usually white, pink, yellow and even black pearls can be found.
A cultured pearl is produced when the irritant is inserted into the oyster which is living in specially created oyster beds. They are generally more uniform in appearance.
Natural pearls are found in wild, untended oyster beds and are considered more valuable.
This hard, usually white substance is the tusk or tooth of a living animal. The elephant, hippopotamus, the walrus and several species of whales were hunted for their ivory.
In recent years, more and more people have begun to consider this a cruel way to get a gem stone and the sale of ivory pieces in many parts of the world has decreased.
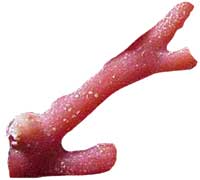
The stone known as coral is actually the skeletal remains of a filter feeding marine animal. Living in colonies, coral can form huge underwater structures, or reefs, stretching for miles. The great barrier reef in Australia is over 1,200 miles (or 2000 kilometers) long.
Coral comes in too many shapes, colors and textures to describe here. In jewelry, whether polished or as found, is a frequent accent piece.
And like many aspects of culture and life, there are many who tried to group a gem stone by type.
This is because the objects that we call gem stones are comprised of a varied list of substances.
Diamond and turquoise do not resemble each other, yet both are considered a gem stone.
The Japanese pearl and the Sri Lankan moonstone may resemble each other, but the pearl is not always considered a gem stone.
So, what are the types of gem stones and how do they relate to each other?
There are several main types of gem stones, and any gem may belong to more than one gem stone type.
Gem Stone Type - Crystalline vs Amorphous:
This is one of the most common distinctions in gem stones. A gem stone of the crystalline type, such as a diamond or a ruby, is made up of a single crystal.
This crystal can be a single element, like the carbon of the diamond, or a chemical compound, like the aluminum oxide of the ruby.
A gem of the amorphous type, like turquoise, is made up of a hardened mixture of other substances. While individual components of this mixture can be crystalline, the gem stone itself is not a single crystal.
Gem Stone Type – Organic vs Inorganic:
Most gem stones are made from non living materials and are called inorganic gems such as aluminum Oxide (ruby, sapphire), beryl (emerald) and quartz (amethyst).
Organic gems are a group of gem stones whose creation is associated with living organisms which are formed from once living material changed over time into a stone.
Amber, a typically clear, yellowish stone, is formed from tree resin fossilized over years.
Jet, a form of coal, is a mineral made from decayed plant material under extreme pressure.
Other organic materials such as pearl, ivory, and coral, are considered by some to be gem stones.
Others feel that to be a true gem, the stone must be formed by gradual processes over long periods of time.
They feel that since pearls and ivory are formed in few years they disqualified them from the gem stone category. But they are still pretty!
Gem Stone Type - Mineral vs Rock:
Like the previous grouping, this gem stone type is determined by the content of the stone.
A mineral gem stone is a single, naturally occurring compound formed through various geological processes.
Diamonds and rubies also fall into this category, as does jade which, while a crystalline mineral, is not composed of a single crystal.
A rock is a cohesive mixture of minerals. An example of this gem stone type is the Lapis Lazuli, one of the first stones to be considered a gem.
Gem Stone Type – Miscellaneous:
Take your pick.
Blue vs. red. Hard vs. soft. Smooth vs. rough. Opaque vs. clear. All are valid comparisons.The most valid of all, perhaps is the preference type.
That is, the type I like vs. the type I don't like.
After all, it's how we perceive the stone that matters.
What makes one thing a precious gem stone and another a semi-precious gem stone or just a rock?
The answer to what makes a gem a precious stone is mostly historic and largely arbitrary.
It was determined by three key factors:
What gem stones are considered precious stones?
First of all, in modern gemology parlance, there is no distinction between precious and semi-precious stones. All stones are considered precious gems by the professional gemologist.
That being said, the classification of stones as precious gems has existed for thousands of years, and is still a concern of collectors.
There are only five stones that were historically considered precious gems:
Made of a crystalline form of carbon, the diamond is the most well known, and arguably the most admired of the precious gemstones.
The word diamond comes from the ancient Greek word adamas, meaning 'impossible to tame'. The English word 'adamant', which means unbreakable or unyielding, comes from the same root.
Diamond gem stone is the hardest naturally occurring substance, making it the most durable of all precious gem stones. The diamond's complex crystalline structure lends itself to multifaceted shapes, also refracts and disperses ambient light, giving it a brilliance that is virtually unmatched among the precious and semi precious gems.
Almost as well known as the diamond, the ruby gemstone also rivals the diamond for hardness, ranking nine on the ten point Mohs hardness scale.
This precious gem stone is a crystalline compound based on the mineral corundum (aluminum oxide) mixed with the metal chromium, which produces the distinct and signature red color.
A close cousin to the ruby, this precious gem stone is also based on corundum. While the blue sapphire gemstone is the best known variety, this precious gem stone comes in a range of colors (fancy sapphires) including pink, orange, purple, yellow, blue and white. In its most pure form, the sapphire is transparent.
Based on the mineral beryl, the emerald gemstone is pound for pound the most valuable gem stone in the world. The characteristic green color of this precious gemstone is caused by traces of chromium and iron.
This precious gem stone is a variety of the common stone quartz. Its typical purplish color is caused by a combination of mineral impurities and crystalline structure. The stone known as burnt amethyst is created by heating the gem, producing a yellowish tint.
So again, what makes a gem a precious stone?
The answer is like the old adage, "Something is worth whatever someone will pay for it."If a stone is precious to you, it is a precious gem stone, regardless of the comments of history.
Even the prettiest of the natural uncut gem stones fall short of our expectations.
This is where gem stone cutting comes in.
The term lapidary covers all of the many techniques used to make a raw gem stone more attractive and useful. While some of the more amorphous stones like turquoise respond well to simple polishing, many of the most valuable must be cut.

The cutting of gem stones is required because many gem stones have a strong and rigid crystalline structure and are too hard and brittle to be shaped any other way.
The principle behind gem stone cuts is based on the way the molecules of stones are 'stacked'; just imagine these molecules as stacked in layers like a deck of cards.
Striking the stone along a line between crystal layers will cause a section of the stone to break away easily and cleanly.
This way, you can cut the gem stone.
Some stones, like mica and quartz, are cut easily due to the weaker bond between the crystalline layers, while others require special tools and skills to produce the gem stone cuts.
Some gem stones with simpler crystalline structures can only be cut in one or a few directions. Others, like the diamond, have a complex structure and can be cut several ways on the same stone.
Each cut is called a facet. Thus the term multi faceted originates as a gem term describing complex cuts of gem stones that can show more than one face or facet.
The reason for gem stone cuts varies from stone to stone. For the diamond, cutting the gem stone is needed to get the brilliance the diamond is famous for.
Other reasons for cutting a gem stone is to achieve a particular shape or style for a specific piece of jewelry.
There are many types of gem stone cuts in common use today.
The gem stone cuts vary from checkerboard cut, brilliant cut, emerald cut, round cut, square cut, triangle cut, rose cut, baguette cut, trilliant cut, marquise cut, heart cut, gem stone cut cabochon, octagon cut, cushion cut, oval cut, princess cut, radiant cut and briolette cut.

Some Types of Gem Stone Cuts:
Checkerboard Cut:
The checkerboard cut is a technique where the gem stone is cut into a multitude of square facets spaced regularly around the stones surface, giving a 'Checkerboard' effect of light and dark squares when moved in the light.
This type of gem stone cuts is commonly used for garnets, topaz, citrines and amethysts or semi precious stones.
Cabochon Cut:
The gem stone cut known as cabochon is one of the most ancient methods of cutting gem stones. It is rounded on the top and flat on the bottom.
Among the gem stones commonly cut in this fashion are the star sapphire, cat's eye gem stones, tiger's eye gem stones, star gem stones and the star ruby.
In recent years, more and more demand for cabochon cut emeralds has emerged in the cut gem market.
Rose Cut:
The rose cut is a variation of the cabochon where flat facets are polished into the curved surface of the cabochon cut stone.Brilliant Cut:
In earlier years, diamonds were cut using the rose cut method, but now the brilliant cut method is commonly used. This is a method of cutting the gem stonein the form of tow truncated cones, face to face, with the upper cone more severely truncated than the lower.
The lower truncated cone forms a facet known as the cutlet. Together, these compound shapes produce the most complete return of light of any gem cutting technique.
So, whether for style, brilliance, or shape, gem stone cutting will always be an integral part of the gem stone industry.
Gem stones are, in general, hard, shiny substances that are often used in jewelry.
While the materials range from fossilized tree sap (as in amber), through pure carbon (as in diamond) and includes various mineral compounds (like aluminum oxide which is the basis of both the sapphire and the ruby).
So what is a crystal gem stone and what meaning does this have on how it is treated?
The crystal gem stone has a meaning that is distinct from other amorphous types of gem stones.
An amorphous gem stone is one that contains a mixture of elements or compounds suspended in a solid form. Like the piece of cement on a sidewalk, all of the ingredients are mixed randomly.
Examples of amorphous gem stones are turquoise and opal.
A crystal is more like a brick wall, where each element is stacked in an even and regular pattern. This type includes quartz, beryl and, of course, the diamond.
Crystals and Gem Stones – Crystal Shape:
Studying crystals and gem stones starts with the shape. Cubic crystalline gem stones break into facets that are parallel and of similar length.The simplest is, of course, the cube (with six faces), but can include shapes with four, eight, twelve, twenty four and as many as forty eight parallel equal sized faces. Diamonds, garnets and the cousin of the ruby, the spinel, are included in this category of crystals and gem stones.
Other crystals with regular faces include the hexagonal and tetragonal, which differ from the others in the number of directions that facets are pointing.
Topaz, jadeite and microline feldspar are examples of gem stones with unevenly sized facets.
Crystals and Gem Stones – Crystal Color:
Several things can affect the color of a crystalline gem stone including material composition, shape, and setting. But the crystal structure of the stone has the most unique effect.The layers of crystals act like tiny mirrors and prisms that bend, reflect, refract and enhance any ambient light that enters the gem. The most distinct example is a certain type of alexandrite which appears blue or green in daylight, but red and purplish in artificial light.
Sapphires, garnets and tourmalines can respond in a similar manner to changes in light.
Crystals and Gem Stones – Crystal Structure:
The effect of the crystalline structure of the gem can affect more than its color and brilliance.It determines how the stone can be worked and shaped by cutting. The process of cutting a gem stone uses the natural planes of the crystal to chip pieces of the hard material off, leaving a clean, flat surface in its place.
The more complex the crystal, the more cutting options are available.
Understanding the structure and physics of the crystal as it pertains to the gem stone has great meaning for the gemologist. When starting with a raw, uncut gem, it determines, to a large degree, what the final product can look like.
Crystals – It's what many gem stones are made of. And the study of crystals and gem stones are what it takes to make those gem stones into jewelry.
So, you have a pretty stone, and you want to know just what it is you have! Maybe it's a diamond gem stone, or an emerald gem stone, or maybe it's a close cousin, or even a piece of colored glass. That's where the science, (and art) of gem stone identification comes in.
If you are confused about the identity of your gem stone, don't feel embarrassed. Kings and emperors have made the same kind of mistakes in identifying gem stones themselves.
Take the ruby. It's a deep red crystal, very hard and very beautiful. And very hard to distinguish from its mineralogical cousin, the very beautiful but somewhat less rare spinel.
Chemically very similar, containing only one extra ingredient in its molecular mix, those who would be experts at identification of gem stones have often mistaken the spinel for the ruby. The most famous case of mistaken identity is the Black Prince Ruby, actually a 170 carat spinel, which has been for centuries a part of the Crown Jewels of England.
So, how does one go about identifying gem stones? Well, it takes some training, some special tools, and a lot of patience.
Identifying Gem Stones – Step 1:
First, try to make sure that, the gemstone that you have, is a gem stone. Some times what you think may be a gem stone is just a pretty rock or a piece of metallic ore.
Since the term gem stone is largely arbitrary, this can be hard. Some basic guidelines include:
Identifying Gem Stones – Step 2:
Hardness:
In the identification of gem stones, hardness is one of the most important of all tests. While not usually a definitive way to identify a gem stone, it does at least put you into the correct group of possibilities.To help you use hardness to identify a gem stone, there are a variety of hardness scales that you can use. The most common is the 'Mohs' Scale' which ranks mineral hardness on a scale of one (talc) to ten (diamond).
To measure the hardness of the gem stone you wish to identify, you will use a hardness kit. This contains a set of substances of varying hardness keyed to one of the hardness scales.
If your test substance can scratch the subject gem stone, then the test substance is harder than the subject gem stone. By trying several test substances on your subject gem stone, you will be able to approximate the hardness of the subject.
Since diamond is often too expensive for most kits, glass is sometimes used in its place.
Identifying Gem Stones – Step 3:
Cleavage:
This refers to the tendency of crystals to break along fixed planes in their structure. By striking the crystalline gem stone, you can examine the break and compare it to various cleavage charts.Many gem stones, including quartz and mica, are easily identified by this way. If you suspect that your gem stone is extremely valuable, like a diamond, you may want to skip this step.
Identifying Gem Stones – Step 4:
Streak:
This is a method of gem stone identification that involves using the subject gem stone to make a mark on a hard, ceramic plate. Many (but not all) gem stones will leave a streak. By comparing the appearance of this streak to various charts, you have another clue to use in gem stone identification.Identifying Gem Stones – Step 5:
Crystal morphology, or shape.
Most gem stones are made up of crystals, each with a unique shape based on their atomic and molecular structure. A simple example of crystal shape can be seen by examining sugar crystals and salt crystals under a powerful glass. While they may look the same in a bowl, up close their crystal shapes are very different and unique.Identifying Gem Stones – Step 6:
Color:
While this may seem the first test to use when classifying a gem stone, using color to identify a stone is not as reliable as you might think.Most people view the sapphire as blue, but this cousin to the ruby can be found in various shades including pink, green, yellow and almost transparent. The classic diamond, with its colorless crystal, looks so much like the less rare cubic zirconium or cubic zirconia, that they almost indistinguishable without a close examination.
Identifying Gem Stones – Step 7:
Chemical and Physical tests:
These methods of identification of gems most often used by experts because they usually require special equipments. The tests include:Once you have your list of measurements, and a reliable set of tables for comparison, you are well on your way to identification of your gem stone.
BUT, before you put the down payment on that boat, check with an expert(gemologist who is a person who studies gems and can identify gem stones) to make sure that the shiny stone that you have, is really a diamond, and not a zirconium.
Note: (Please, don't try to identify a gem stone by yourself if you have precious stones and expensive ones, but it's better to check them by a gemologist or send your gem stones to us to check them for you).
 Purple Russian Alexandrite-squares |
Blue Russian Alexandrite-squares
|
 Purple Russian Alexandrite |
Blue Russian Alexandrite
|
 Purple Heart Alexandrite |  Blue Heart Alexandrite |
 Red Alexandrite gemstone-square |
Green Alexandrite gemstone-square
|
 Red Alexandrite gemstone-oval |  Green Alexandrite gemstone-oval |
 Synthetic Ruby gemstone |  Synthetic Opal gemstone |
 Synthetic Emerald gemstone |  CZ-Cubic Zironia Pink |
 Multi Color of CZ | 
CZ-Cubic Zirconia Yellow |